VPS36
Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens
| VPS36 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | VPS36, C13orf9, EAP45, CGI-145, vacuolar protein sorting 36 homolog | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 610903; MGI: 1917410; HomoloGene: 9374; GeneCards: VPS36; OMA:VPS36 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vacuolar protein-sorting-associated protein 36 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VPS36 gene.[5][6][7]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000136100 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000031479 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Kamura T, Burian D, Khalili H, Schmidt SL, Sato S, Liu WJ, Conrad MN, Conaway RC, Conaway JW, Shilatifard A (May 2001). "Cloning and characterization of ELL-associated proteins EAP45 and EAP20. a role for yeast EAP-like proteins in regulation of gene expression by glucose". J Biol Chem. 276 (19): 16528–33. doi:10.1074/jbc.M010142200. PMID 11278625.
- ^ Slagsvold T, Aasland R, Hirano S, Bache KG, Raiborg C, Trambaiolo D, Wakatsuki S, Stenmark H (May 2005). "Eap45 in mammalian ESCRT-II binds ubiquitin via a phosphoinositide-interacting GLUE domain". J Biol Chem. 280 (20): 19600–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.M501510200. PMID 15755741.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: VPS36 vacuolar protein sorting 36 homolog (S. cerevisiae)".
Further reading
- Lai CH, Chou CY, Ch'ang LY, et al. (2000). "Identification of novel human genes evolutionarily conserved in Caenorhabditis elegans by comparative proteomics". Genome Res. 10 (5): 703–13. doi:10.1101/gr.10.5.703. PMC 310876. PMID 10810093.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- von Schwedler UK, Stuchell M, Müller B, et al. (2003). "The protein network of HIV budding". Cell. 114 (6): 701–13. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00714-1. PMID 14505570.
- Martin-Serrano J, Yarovoy A, Perez-Caballero D, et al. (2003). "Divergent retroviral late-budding domains recruit vacuolar protein sorting factors by using alternative adaptor proteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100 (21): 12414–9. Bibcode:2003PNAS..10012414M. doi:10.1073/pnas.2133846100. PMC 218772. PMID 14519844.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Dunham A, Matthews LH, Burton J, et al. (2004). "The DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 13". Nature. 428 (6982): 522–8. Bibcode:2004Natur.428..522D. doi:10.1038/nature02379. PMC 2665288. PMID 15057823.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Bowers K, Piper SC, Edeling MA, et al. (2006). "Degradation of endocytosed epidermal growth factor and virally ubiquitinated major histocompatibility complex class I is independent of mammalian ESCRTII". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (8): 5094–105. doi:10.1074/jbc.M508632200. PMID 16371348.
- Alam SL, Langelier C, Whitby FG, et al. (2007). "Structural basis for ubiquitin recognition by the human ESCRT-II EAP45 GLUE domain". Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13 (11): 1029–30. doi:10.1038/nsmb1160. PMID 17057716. S2CID 41152121.
- v
- t
- e
PDB gallery
-
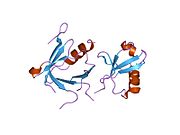 2dx5: The complex structure between the mouse EAP45-GLUE domain and ubiquitin
2dx5: The complex structure between the mouse EAP45-GLUE domain and ubiquitin -
 2hth: Structural basis for ubiquitin recognition by the human EAP45/ESCRT-II GLUE domain
2hth: Structural basis for ubiquitin recognition by the human EAP45/ESCRT-II GLUE domain
 | This article on a gene on human chromosome 13 is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e